Technical analysis is a method used by investors and traders in financial markets to forecast future price movements by examining past market data such as price movements and trading volume. In this article, we will discuss what technical analysis is, how it is done, and the essential elements for successful technical analysis.
Table of Contents
- Definition and Purpose of Technical Analysis
- Basic Principles of Technical Analysis
- Tools and Indicators Used in Technical Analysis
- Types of Charts and Their Uses
- Support and Resistance Levels
- Trend Analysis and Trend Lines
- Patterns and Formations
- Trading Strategies and Risk Management
- Differences Between Technical Analysis and Fundamental Analysis
- Technical Analysis Software and Platforms
- Time Frames in Technical Analysis
- Books and Resources on Technical Analysis
- Tips for Success in Technical Analysis
- Technical Analysis and Artificial Intelligence
- Technical Analysis and Algorithmic Trading
- Education and Certification in Technical Analysis
- Psychology in Technical Analysis
- Developing Strategies in Technical Analysis
- Conclusion and Recommendations
1. Definition and Purpose of Technical Analysis
Technical analysis is a method of forecasting future price movements by analyzing past price movements and trading volumes. The primary goal of this method is to identify market trends and potential reversal points to make informed investment decisions. Technical analysis is typically used by short-term investors and traders because it is more suitable for predicting short-term price fluctuations.
2. Basic Principles of Technical Analysis
The basic principles of technical analysis are based on the idea that market prices reflect all available information, price movements follow specific patterns, and history tends to repeat itself. These principles are:
2.1. Prices Reflect Everything: Market prices include all available information and move accordingly.
2.2. Price Movements Follow Patterns: By looking at past price movements, it is possible to predict how prices may move under similar conditions in the future.
2.3. History Repeats Itself: Human psychology and market behavior generally remain the same, so past price movements can occur similarly in the future.
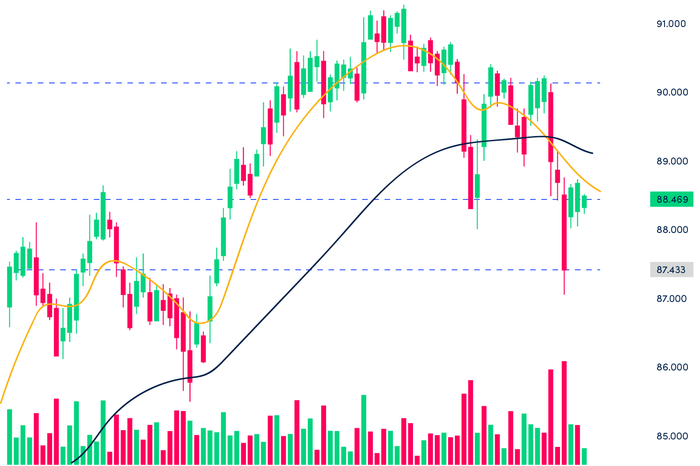
3. Tools and Indicators Used in Technical Analysis
There are many tools and indicators used in technical analysis. These tools and indicators help investors better understand the market and make informed investment decisions. The most commonly used tools and indicators are:
3.1. Moving Averages (MA)
3.2. Relative Strength Index (RSI)
3.3. Moving Average Convergence Divergence (MACD)
3.4. Bollinger Bands
3.5. Fibonacci Retracement Levels
3.6. Stochastic Oscillator
4. Types of Charts and Their Uses
The most commonly used types of charts in technical analysis help investors visually analyze price movements. The main types of charts are:
4.1. Line Charts: Connect the closing prices with a line. They are simple and easy to understand.
4.2. Bar Charts: Each bar represents the opening, closing, highest, and lowest prices for a specific time period.
4.3. Candlestick Charts: Similar to bar charts but provide more detailed information. They better reflect price movements and market sentiment.
5. Support and Resistance Levels
Support and resistance levels are important levels where price movements tend to stop or reverse. A support level is where the price stops falling or rebounds. A resistance level is where the price stops rising or pulls back. These levels are critical decision points for investors.
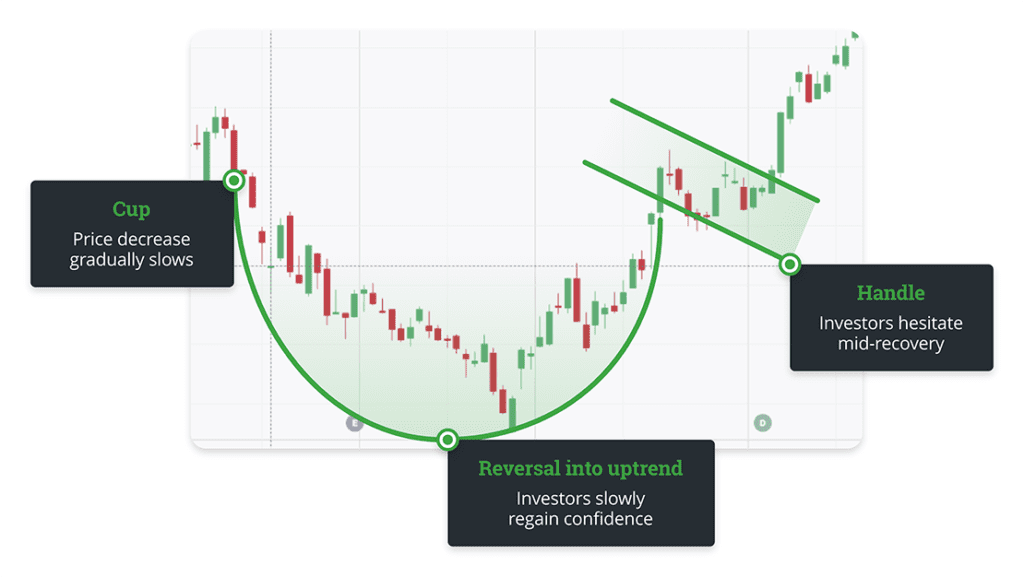
6. Trend Analysis and Trend Lines
Trend analysis is a technique to identify the general direction of the market. There are three main types of trends:
6.1. Uptrend: A trend where prices generally move upward.
6.2. Downtrend: A trend where prices generally move downward.
6.3. Sideways Trend: A trend where prices fluctuate within a certain range without a clear direction.
Trend lines are simple lines that help identify and visualize these trends. In an uptrend, the trend line connects support levels. In a downtrend, it connects resistance levels.
7. Patterns and Formations
In technical analysis, patterns and formations are specific recurring patterns in price charts. These formations are used to predict future price movements. The most common patterns and formations are:
7.1. Head and Shoulders
7.2. Double Top and Double Bottom
7.3. Triangles
7.4. Flags and Pennants
8. Trading Strategies and Risk Management
To be successful in technical analysis, it is essential to develop effective trading strategies and manage risks properly. Trading strategies involve making buy and sell decisions based on specific indicators and analyses. Risk management helps investors minimize potential losses. The main risk management techniques are:
8.1. Stop-Loss Orders
8.2. Position Sizing
8.3. Take-Profit Orders
9. Differences Between Technical Analysis and Fundamental Analysis
While technical analysis focuses on price movements and market data, fundamental analysis focuses on financial conditions and economic indicators to determine the value of an asset. Fundamental analysis is typically used by long-term investors, while technical analysis is preferred by short-term traders.

10. Technical Analysis Software and Platforms
Various software and platforms are used for technical analysis. These tools help investors and traders analyze price movements and make decisions. The most popular technical analysis software and platforms are:
10.1. MetaTrader: One of the most widely used platforms in the forex and stock markets. MetaTrader offers numerous indicators and tools.
10.2. TradingView: Known for its user-friendly interface and comprehensive charting features. Its social platform features allow users to share their analyses and see others’ analyses.
10.3. Thinkorswim: A comprehensive platform for derivative markets and stock trading. It is especially popular in the US markets.
11. Time Frames in Technical Analysis
Choosing the right time frame in technical analysis is crucial for the success of the strategy. Different time frames are used for different types of investors:
11.1. Scalping: Suitable for traders aiming to profit from small price movements by making very short-term (minute-by-minute) trades.
11.2. Day Trading: Used by investors aiming to profit from daily price fluctuations by making trades within a day.
11.3. Swing Trading: Suitable for investors holding positions for several days to a few weeks. It aims to take advantage of medium-term price movements.
11.4. Long-Term Investment: Suitable for investors planning to hold positions for months or years. It aims to benefit from large market trends.

12. Books and Resources on Technical Analysis
To improve your knowledge of technical analysis, here are some important books and resources:
12.1. “Technical Analysis of the Financial Markets” by John Murphy: A classic book that thoroughly covers the basics and applications of technical analysis.
12.2. “A Complete Guide to Volume Price Analysis” by Anna Coulling: A comprehensive resource for understanding the relationship between volume and price.
12.3. “Japanese Candlestick Charting Techniques” by Steve Nison: Provides detailed information about candlestick charts and their use.
12.4. Online Courses and Websites: You can find technical analysis courses on platforms like Udemy and Coursera, and analyze community analyses on websites like TradingView.
13. Tips for Success in Technical Analysis
Here are some tips to consider for success in technical analysis:
13.1. Make a Plan: Make a plan before each trade and stick to it. Your plan should include your entry and exit points, stop-loss, and take-profit levels.
13.2. Control Your Emotions: Emotional decisions in the market can lead to significant losses. Trust your analysis and strategy.
13.3. Keep Records: Record your trades and their outcomes. This helps you make more informed decisions in future trades.
13.4. Follow Market News: Keeping up with market news and economic data while doing technical analysis helps you be prepared for sudden price movements.
14. Technical Analysis and Artificial Intelligence
In recent years, artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning (ML) have increasingly been used in technical analysis. These technologies can effectively analyze large datasets and make market predictions using complex algorithms. AI applications provide investors with more accurate and faster analyses, ensuring they do not miss potential investment opportunities.
15. Technical Analysis and Algorithmic Trading
Algorithmic trading involves automated buy and sell orders based on specific rules and algorithms. Technical analysis indicators and signals can form the basis of these algorithms. The advantages of algorithmic trading include:
15.1. Speed: Automated systems can trade much faster than humans.
15.2. Discipline: Since trading is based on predefined rules, emotional mistakes are minimized.
15.3. Efficiency: Analyzing large amounts of data to determine the best trading opportunities.
16. Education and Certification in Technical Analysis
There are various education programs and certifications available to gain advanced knowledge in technical analysis and advance your career in this field. Some prominent programs include:
16.1. Chartered Market Technician (CMT): Offered by the CMT Association, this program provides in-depth knowledge of technical analysis and has international recognition.
16.2. Certified Financial Technician (CFTe): Offered by the International Federation of Technical Analysts (IFTA), this certification is another globally recognized technical analysis program.
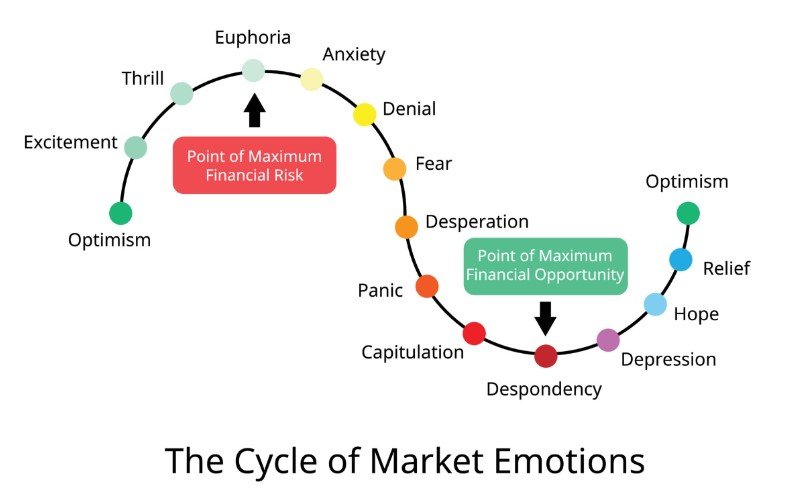
17. Psychology in Technical Analysis
Investor psychology plays a significant role in technical analysis. Understanding the behavior and psychological tendencies of market participants helps make more accurate predictions. Some psychological factors to consider in technical analysis are:
17.1. Fear and Greed: These are the primary emotions influencing the decisions of market participants. You can see the effects of these emotions in price movements.
17.2. Herd Behavior: The tendency of a large majority of investors to move in the same direction. This behavior can increase market trends and volatility.
17.3. Psychological Support and Resistance Levels: Specific price levels are points where investors react psychologically. These levels play an essential role in price movements.
18. Developing Strategies in Technical Analysis
Technical analysis helps investors and traders develop personal trading strategies. To develop an effective strategy, you can follow these steps:
18.1. Set Your Goals: Clarify your investment goals (short-term profit, long-term growth, risk management, etc.).
18.2. Choose Your Indicators: Select indicators that suit your analysis style and market conditions.
18.3. Define Entry and Exit Rules: Determine under what conditions you will trade and when you will close your positions.
18.4. Apply Risk Management: Determine how much risk you will take in each trade and set your stop-loss levels in advance.
18.5. Test Your Strategy: Test your strategy on demo accounts or historical data and analyze the results.
19. Conclusion and Recommendations
Technical analysis is an essential tool for success in financial markets, but it is not sufficient on its own. It is important to use it together with other analysis methods and evaluate the market from a broad perspective. In this guide, we covered the basic principles of technical analysis, the tools used, and the strategies necessary for success. Continue to learn and practice to master technical analysis.





