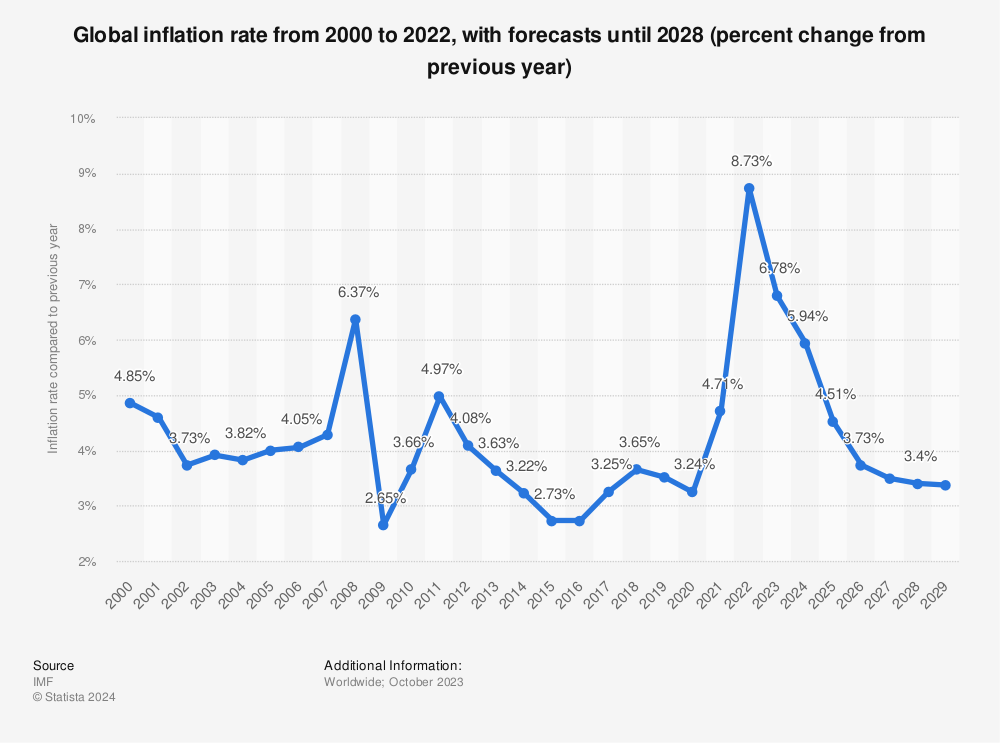
Global inflation has been a significant concern for policymakers, investors, and consumers alike. As we move through 2024, understanding the effects of inflation on economic growth is crucial for making informed decisions. This blog post explores the current trends in global inflation and their implications for economic growth, drawing on recent analyses and forecasts from various sources including the International Monetary Fund (IMF), J.P. Morgan, and the Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development (OECD).
Current Inflation Trends
Declining Inflation Rates
In 2024, global inflation is projected to decline from its peaks, driven by easing supply chain disruptions and lower energy prices. The International Monetary Fund (IMF) forecasts global headline inflation to fall to 5.8% in 2024, down from 6.8% in 2023. Similarly, J.P. Morgan Research anticipates that global core inflation will remain around 3% throughout the year.
Regional Variations
While the overall trend points towards lower inflation, significant regional differences persist. For instance, inflation in emerging markets, excluding China and Turkey, is expected to decline by about 100 basis points in 2024. In contrast, inflationary pressures in China are projected to ease slightly, with core CPI expected to trend up modestly. The United States and the Eurozone are also seeing a gradual decline in inflation, though it remains above the central banks’ targets.
Economic Growth Prospects
Impact on Developed Economies
In developed economies, the decline in inflation is expected to bring some relief. The OECD projects steady global GDP growth of 3.1% in 2024, consistent with the previous year. However, tight monetary conditions, particularly high interest rates to combat inflation, continue to weigh on economic activity. The growth forecast for advanced economies remains modest, reflecting these ongoing challenges.
Emerging Markets
Emerging markets are anticipated to drive much of the global economic growth. The IMF forecasts that these economies will see higher growth rates compared to developed nations. This growth is buoyed by strong domestic demand and increased investment in infrastructure and technology. However, these economies are also more vulnerable to external shocks and inflationary pressures, which could dampen their growth prospects.
Factors Influencing the Inflation-Growth Relationship
Monetary Policy
Central banks worldwide are balancing the act of controlling inflation without stifling economic growth. The Federal Reserve and the European Central Bank have implemented a series of interest rate hikes over the past years to curb inflation. While these measures are effective in reducing inflation, they also increase borrowing costs, which can slow down economic growth. The effectiveness of these policies will be crucial in determining the economic trajectory for 2024 and beyond.
Supply Chain Dynamics
Improvements in global supply chains have played a significant role in reducing inflationary pressures. The normalization of supply chains has helped stabilize prices of goods and services, contributing to lower inflation. However, any disruptions in supply chains due to geopolitical tensions or other factors could reignite inflationary pressures and impact economic growth negatively.
Energy Prices
Energy prices, particularly oil and gas, have a significant impact on inflation. In 2024, global energy prices have stabilized, contributing to lower inflation rates. However, any significant changes in energy prices could affect inflation and economic growth. The transition to renewable energy sources is also playing a role in stabilizing energy prices and reducing inflationary pressures.
Implications for Investors
Stock Markets
Lower inflation generally leads to lower interest rates, which can boost stock markets. However, the relationship is complex, as high inflation can lead to higher interest rates, which can negatively impact stock markets. Investors should keep an eye on inflation trends and central bank policies to make informed investment decisions.
Bonds and Fixed Income
In a high inflation environment, the value of fixed income investments, such as bonds, can decline. Conversely, lower inflation can lead to lower interest rates, which can boost the value of existing bonds. Investors should diversify their portfolios to hedge against inflation risks.
Future Outlook
Continued Monitoring
The relationship between global inflation and economic growth is complex and multifaceted. Policymakers, investors, and businesses should continue to monitor these trends closely. While the decline in inflation provides some relief, high interest rates and tight monetary policies continue to pose challenges for economic growth, particularly in developed economies.
Technological Advancements
Technological advancements can also play a role in mitigating inflationary pressures and boosting economic growth. Innovations in supply chain management, energy production, and financial technologies can enhance efficiency and reduce costs, contributing to lower inflation and higher economic growth.
Conclusion
The relationship between global inflation and economic growth is intricate and influenced by various factors, including monetary policies, supply chain dynamics, and energy prices. While the decline in inflation provides some relief, the high interest rates and tight monetary policies continue to pose challenges for economic growth, particularly in developed economies. Emerging markets, on the other hand, are expected to drive much of the global economic growth, although they remain susceptible to external shocks and inflationary pressures.
As we navigate through 2024, understanding these dynamics will be crucial for policymakers, investors, and businesses. By staying informed and adaptive, stakeholders can better manage the risks and opportunities presented by the evolving economic landscape.
This comprehensive overview aims to provide a deeper understanding of the current trends in global inflation and their implications for economic growth.